
Read More
Avicenna was a Persian philosopher and physician and was the first recorded person to define the difference between hypnosis and sleep.

Read More
Paracelsus was the first person to use magnets in his work. Many people claimed the healing technique of passing lodestones over the body cured their ailments.
Read More
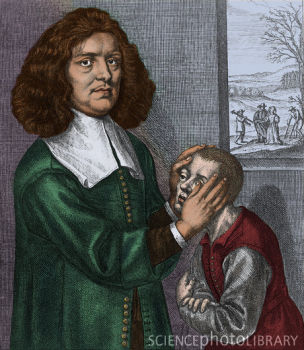
Valentine Greatrakes was an Irish faith healer who toured England and claimed to heal people simply by laying on of hands. Later he would be known as the Great Irish Stroker because he passed magnets over their bodies in order to cure them.
Read More
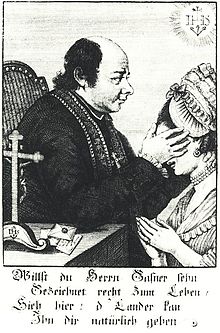
Johann Joseph Gassner was a Catholic priest who believed that disease was caused by evil spirits and could be removed by the use of exorcism.

Read More
Father Maximillian Hell was a Jesuit and applied metal plates to the body and passed magnets over them in order to induce healing. One of his students was Mesmer.

Read More
Marquis de Puységur was a student of Mesmer and was the first to coin the term somnambulism. In fact he called it “artificial somnambulism” which later became known as hypnosis.

Read More
James Braid was a Scottish surgeon was an important influence in hypnosis and hypnotherapy. He coined the phrase neuro-hypnosis (meaning nervous sleep) and shortened it to hypnosis. He discovered that hypnosis has nothing to do with sleep and wanted to call his discovery “monoideism” but the hypnosis name stuck. He believed that the earliest record of hypnosis being used was by the Hindus in ancient India who used hypnotic suggestion to heal sick people in their sleep temples.
James Braid also documented James Esdaile’s work in India.

Read More
Franz Anton Mesmer was an Austrian physicist and started working with magnets around 1770. He called his findings “animal magnestism” (animus meaning to breathe) and “mesmerism”. He found that when a patient’s vein was opened up and bled for a while, passing a magnet over the vein stopped the bleeding. Later he found he could substitute the magnet with a stick with the same result.

Read More
John Elliotson was an English physician who studied mesmerism and used Esdaile’s mesmeric coma. Unfortunately, due to him choosing mainly working class female Irish immigrants and his comments that they were more mechanical led to his demise. John Elliotson is remembered for being the first to advocate the stethoscope.

Read More
Dr. James Esdaile was a Scottish surgeon working out in India. Before the days of chemical anaesthetics, the death rate from complications was 95%. James Esdaile discovered that, by using what he coined “mesmeric coma” the death rate in surgery dropped to 5%. James Esdaile unwittingly contributed to what the medical world now called clinical coma.

Read More
Jean-Martin Charcot was a French neurologist who endorsed hypnotism for the treatment of hysteria.

Read More
Pope Pius XI in 1847 decreed that "Having removed all misconception, foretelling of the future, explicit or implicit invocation of the devil, the use of animal magnetism (Hypnosis) is indeed merely an act of making use of physical media that are otherwise licit and hence it is not morally forbidden, provided it does not tend toward an illicit end or toward anything depraved."

Read More
Ambroise-Auguste Liébeault (1864-1904) co-founded the Nancy school (a school of suggestive psychotherapy) along with Hippolyte Bernheim (1840 – 1919) and first wrote about the necessity for co-operation between the hypnotist and the client for rapport.

Read More
William James was an American psychologist and philosopher who write in detail about hypnosis in his book “Principles of Psychology”.

Read More
Emile Coué was a French pharmacist and founded the New Nancy school. He broke away from hypnosis and called his method “conscious autosuggestion” and was influential with the early 20th Century self-help teachers.

Read More
Ivan Petrovich Pavlov was a Russian psychologist and physician. Ivan is best remembered for his "classical conditioning" – a form of associated learning (often called Pavlovian) from the experiments on salivation from his dogs.

Read More
Sigmund Freud was and Austrian neurologist who studied under Charcot and later witnessed hypnotic experiments carried out by Liébeault and Bernheim in Nancy. Freud developed abreaction therapy using hypnosis with Josef Breuer. When Freud discounted hypnosis in the treatment of psychiatry, stage hypnotists kept it more alive than physicians.

Read More
Pierre Janet was a pioneering French psychologist that coined the phrases "dissociation" and "subconscious"
First International Congress1889
Read More
First International Congress for Experimental and Therapeutic Hypnosis was held in Paris, France. Attendees included Jean-Martin Charcot, Hippolyte Bernheim, Sigmund Freud and Ambroise-Auguste Liébeault.
British Hypnotism Act1952
Read More
British Hypnotism Act was instituted to regulate the practises of stage hypnotists.
British Medical Association1955
Read More
British Medical Association approved the use of hypnosis in the areas of psychoneuroses and hypno-anaesthesia in pain management in childbirth and surgery.

Read More
Pope Pius XII (1955) approved the use of hypnosis by health care professionals for diagnosis and treatment.

Read More
American Medical Association approved a report on the medical uses of hypnosis. It encouraged research on hypnosis although pointing out that some aspects of hypnosis are unknown and controversial.

Read More
Dave Elman was born Dave Kopelman but shortened it when his billing as "The World’s Youngest and Fastest hypnotist" didn’t fit the billboard in 1922. He is remembered for his promotion of medical use hypnosis in the 1960s.
Elman’s definition of hypnosis is still used today by professional hypnotherapists. Although Elman had no medical training but he is known for having trained the most physicians and psychotherapists in America in the use of hypnotism. He is also known for introducing rapid inductions to the field of hypnotism. An induction method he introduced over fifty years ago is still one of the favoured inductions used by many of today’s practitioners.

Read More
Milton Erickson developed a unique and personal approach to hypnosis and has greatly influenced modern hypnosis practises. His hypnotic manner was developed from suffering two counts of Polio and would watch how others in his family functioned and developed his own skills to help others through the power of the unconscious mind.

Read More
One of the pioneers that hasn't received much credit is Charles Tebbetts, the founder of parts therapy. He pursued a career in music when his father died when he was 14 and got a lucky break in an orchestra. In 1960s-70s he pioneered a technique based on the work of Paul Federn, which he coined ego parts. Thus, Tebbetts became the pioneer of parts therapy.

Read More
Walter Andrew Sichort Snr. Little is known about Walter Sichort other than his discovery of that state that is named after him, and his one hypnotic subject and partner, Sarah Zane. He was influential in teaching James Ramey.

Read More
James R Ramey was responsible for the advancement of the Ultra Depth® Process from the work done by Walter Sichort and his assistant Sarah Zane. The Ultra Depth® Process is the process of obtaining hypnotic states deeper than somnambulism.

Read More
Gerald Kein was a hypnosis teacher that taught thousands of people hypnosis. He founded the Omni Hypnosis Training Center back in 1979 and in 1988 he introduced step-by-step how-to seminars on hypnosis on his website for his students. Gerald Kein also created his own version of James Ramey’s UltraDepth Process to just capture the state of deep hypnosis which he called UltraHeight. He could then sell the video for just $45.
Previous
Next
